Internal Linking for SEO: Best Practices & Benefits

Think about all of the ways you can optimise a website. As you mentally run through that list, how high up did you place internal linking? If it’s not one of your utmost priorities, your website’s rankings will be suffering.
In this post, you’ll learn how to easily improve the internal linking on your website, for better SEO results.
What is Internal Linking?
To master internal linking, you must first understand what it is. An internal link on a website is a link that will take a site user from one page on a domain to another page on the same domain. This type of link is a valuable navigation tool, and it assists a search engine logically move about your domain.
Why Do Internal Links Matter?
There are a few things internal links can do for your website.
- Internal links can give your visitors more information on a topic. For example, you run a site about pet care and post about dog grooming tips. By adding internal links to other dog grooming information you have posted, or top-selling grooming products, you give your customer more information that they can browse on your site. This can lead to increased sales and conversions.
- You can experience improved SEO rankings when you consistently use internal linking. When a customer lands on your page and finds internal links to other relevant information, they are more likely to stay on your site. This reduces the bounce rate and increases the time spent on the site. These factors can help your SEO.
- Placing an internal link is a sign to Google that the page you are linking to is useful to your reader. You believe it is so helpful that the reader may want to stop what they are reading and look at the linked page immediately. This can build trust with the search engine giant.
- Google can crawl your site easier. If your website is a tangled mess of seemingly irrelevant links put forth in no particular order, Google will struggle to crawl your site, and the data they extract will be spotty at best. However, when your website is developed with a clear site hierarchy and internal links backing up newer information, Google will better understand your business. Therefore, more relevant information about your products or services will be presented to potential customers on Google’s SERPs.
- When Google crawls your pet care site and identifies several internal links pointing to the same page using the anchor text “pet care”, it understands that page is about pet care and will be relevant for customers searching for queries related to pet care. Google explains this concept in its Links Report, saying that a pages’ relative importance is often related to the number of internal links that lead to the page. Therefore, you can suggest to Google the most important pages on your website, and achieve higher SEO rankings for those pages as a result.
Keys to Using Internal Links to Your Advantage
- Start With Great Content – If you have numerous pages of well-written pet care tips or a number of useful instructional how-to videos, then you have a strong foundation for internal linking that seems natural, is helpful, and makes sense. Unfortunately, the converse is true. Thin content has no redeeming value in your website. No matter how many times you may hear otherwise, content is still essential to your business’ SEO.
- Make Sure Your Links Are Natural – Both Google and visitors to your site can spot pointless fluff crammed with keywords. One way to be sure your internal links are natural is to link using a few words of anchor text. Doing this increases the chances of your reader following a link that directly relates to the information they are seeking.
For example, your customer reads a post about how to prevent a dog’s fur from going all over the house. As the topic relates to shedding, you may want to add a link to a piece of text talking about the best dog grooming tools like brushes for de-shedding, shampoos to lower shedding or wholistic foods to help a dog’s coat.
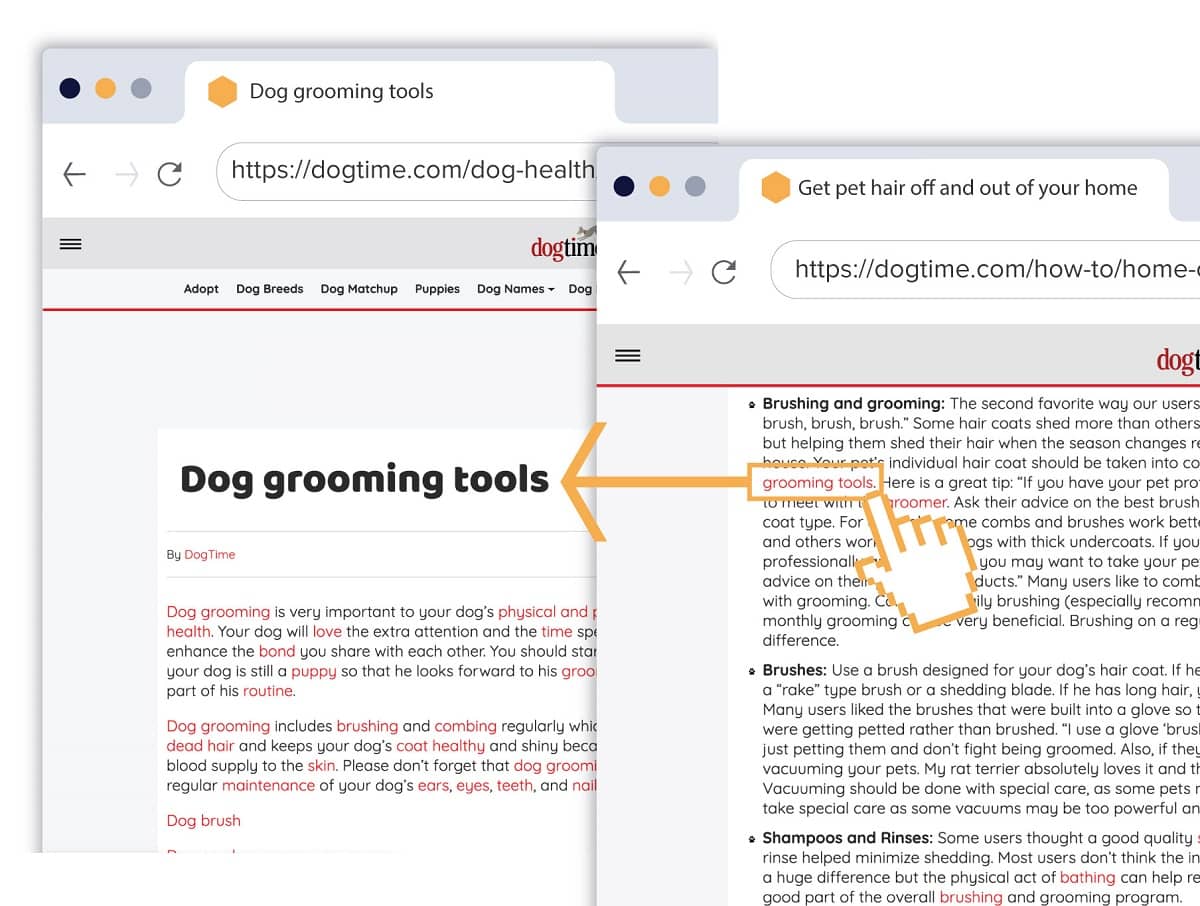
Internally linking to relevant follow-up information from a blog post. For a closer look, visit this page here.
In this example, your site visitor gets useful information. It is also likely that the reader will stay on your site viewing related pages. Should they find your information especially helpful they may purchase a product, recommend your site to others, or leave a positive review.
- Use Relevant Links – It should go without saying that ALL of your links ought to be relevant. However, it bears repeating, an internal link for the sake of adding a link will not improve the customer experience. If anything, pointless links will annoy those visiting your site. Two examples of this are:
- Linking to the homepage of your site
- Linking to the contact us page on your website (when it is not necessary to do so)
- Add a Moderate Number of Links – More advice from Google, “Keep the links on a given page to a reasonable number.” The number of links Google believes to be reasonable is really anyone’s guess. Still, the tidbit of guidance from Google points to the fact that linking overkill is possible. Before you link, ask yourself if it improves the user experience (remember, user experience is a huge part of the upcoming Google algorithm change). If you believe the link is valuable to your reader, then you should go forward with linking.
Case Study
Recently, I implemented more internal links on a client’s website, Online Flooring Store. The results speak for themselves.
Where did I insert more internal links?
1. Products Pages:
-
- A breadcrumb was added to the top of every product page. This included links to the homepage, product category page and brand page.
- Links to view more products of the same type and brand were added directly beneath the product name. This allowed customers to easily navigate between similar products.
- After liaising with the customer service team, we identified that prospective customers often asked questions relating to delivery costs and timeframes. As such, a link to a dedicated shipping FAQs page was added.
- A WordPress plugin was installed that automatically suggested similar products that the customer may wish to browse.
- Internal links in product descriptions were added where relevant. This included links to blog posts, related products, and FAQ pages.
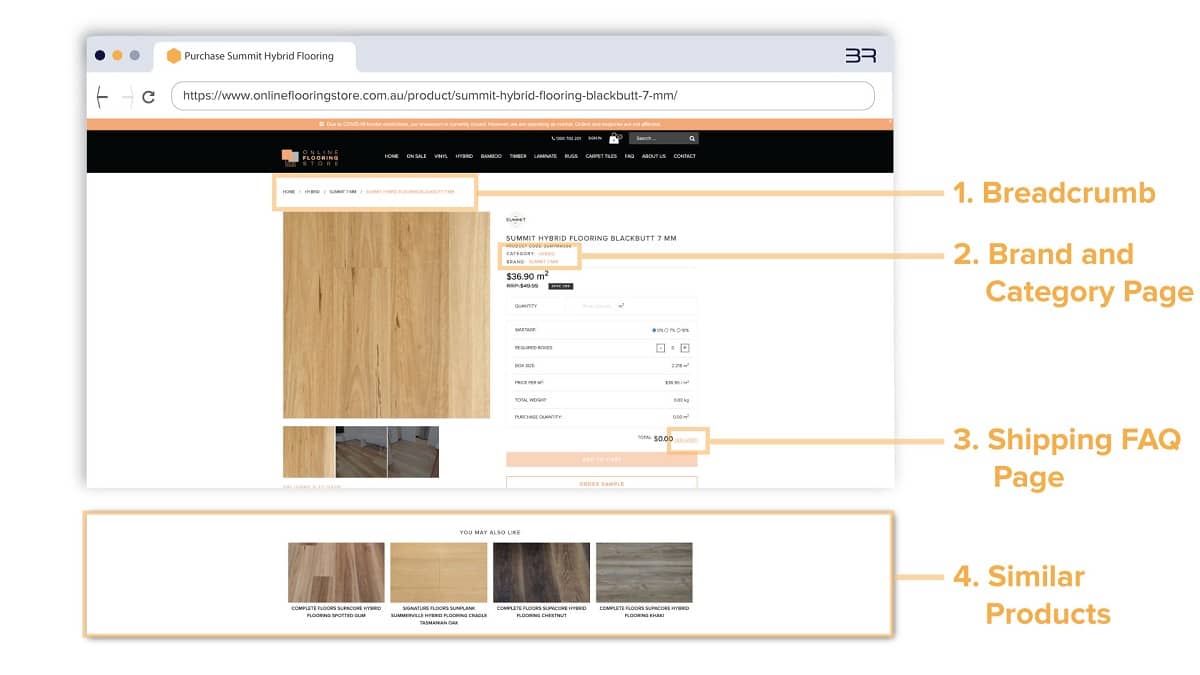
An e-commerce product page with additional internal links. For a closer look, visit this page here.
2. Blog Posts:
-
- The number of internal links to products, brands, category pages, other blog posts, and FAQs pages was increased in all existing and new blog posts.
- Blog categories were updated to include internal links to highlighted blog posts within that category.
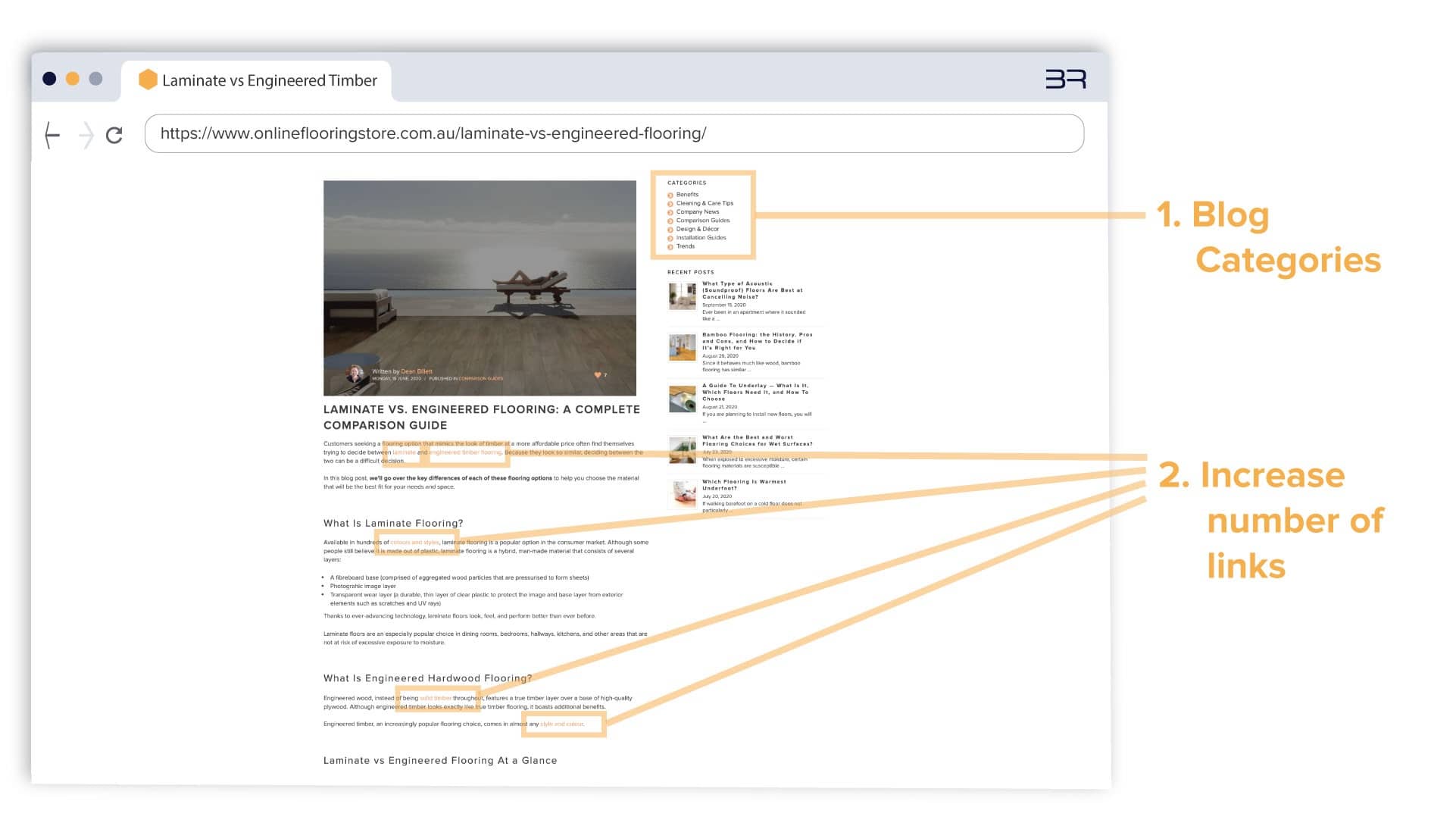
Links to relevant information was increased on all blog posts. For a closer look, visit this page here.
3. Categories:
-
- Product categories were updated to include more links to popular products.
- Brand categories were updated to include links to popular colours within a particular brand.
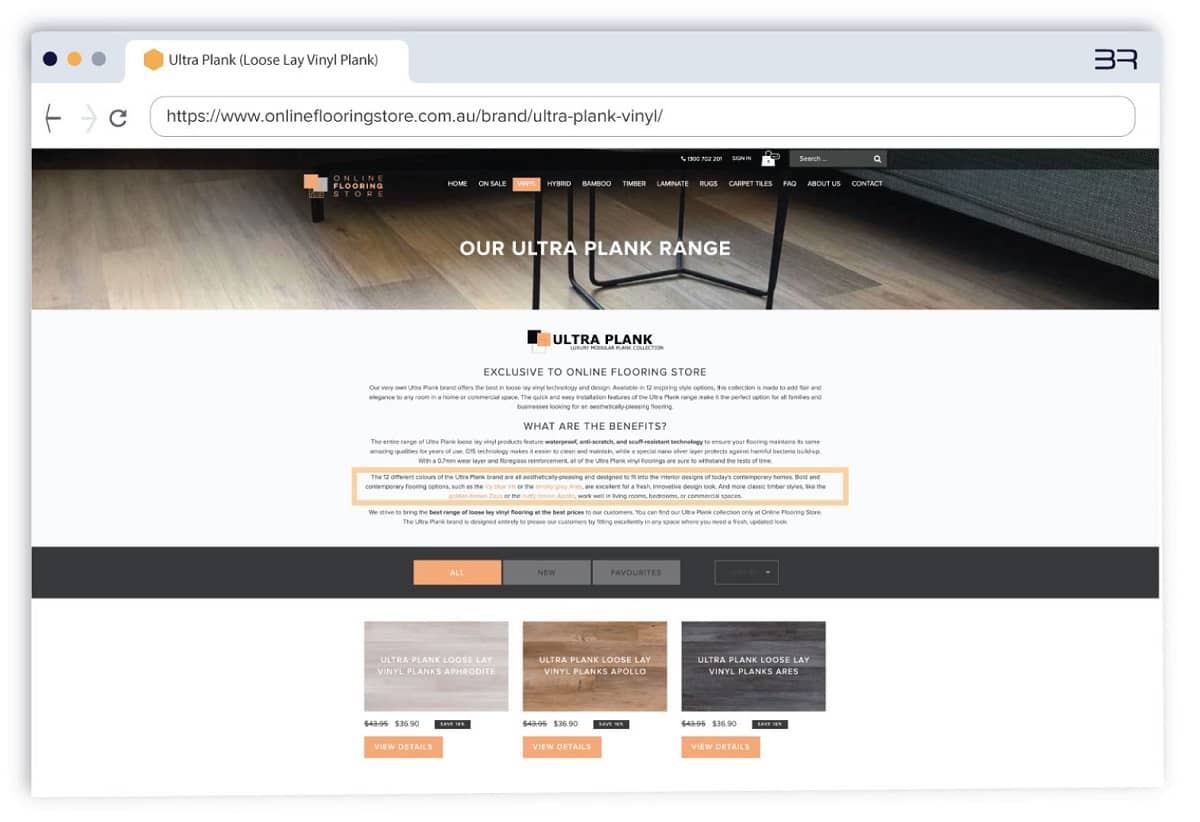
Popular colours were linked to from brand category descriptions. For a closer look, visit this page here.